Synchronizers
Synchronize is defined as “to agree in time or to make agree in time.” Since the input and output shafts are rotating at different speeds the synchronizer must make the two shafts agree in time (speed) so they can be locked together.
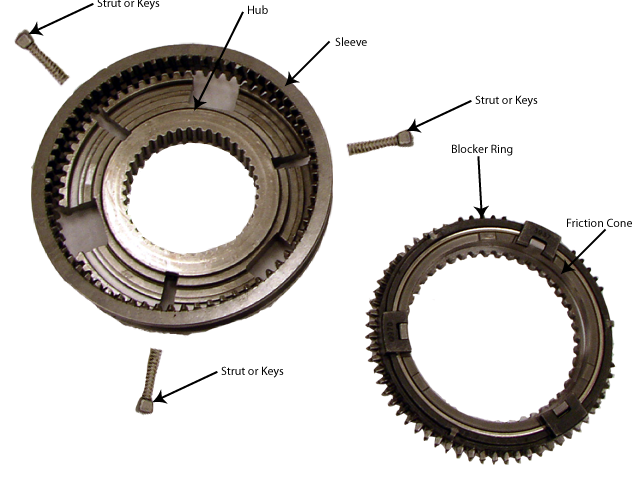
The parts of a synchronizer are:
When the shift fork moves the synchronizer sleeve, the synchronizer begins to speed up or slow down the selected gear. The synchronizer does this by having the hub splined to the output shaft and moving the blocker ring into contact with the gear’s friction cone. As the blocker ring and the friction cone come together, the gear speed is brought up or down to match the speed of the synchronizer. As the speeds match, the splines on the inside of the synchronizer sleeve become aligned with the teeth on the blocker ring and friction cone. The sleeve slides over the teeth, locking the gear to the output shaft, through the synchronizer.
Counter Shaft – G56 Transmission Shown

